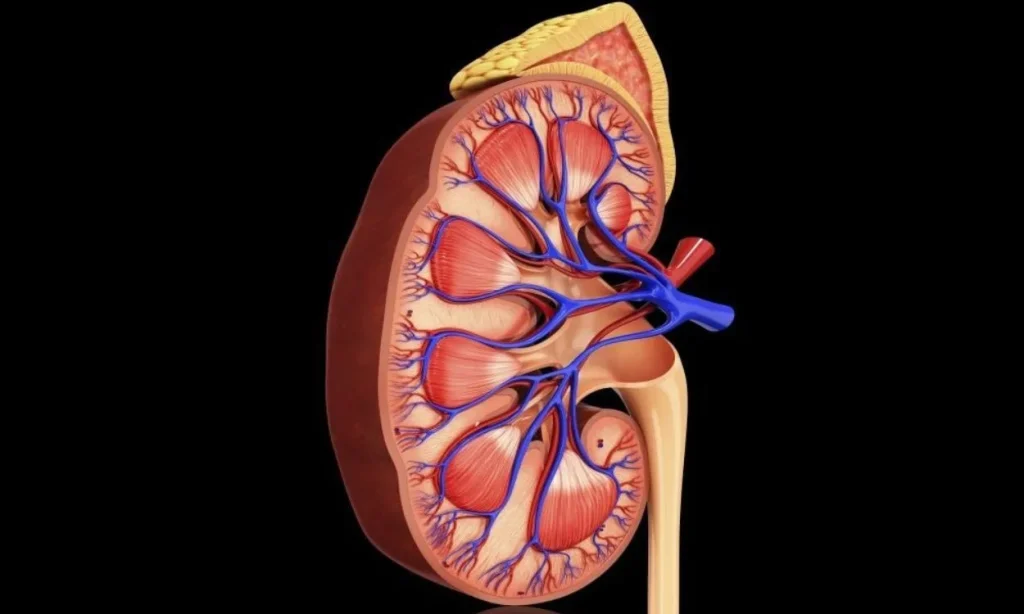
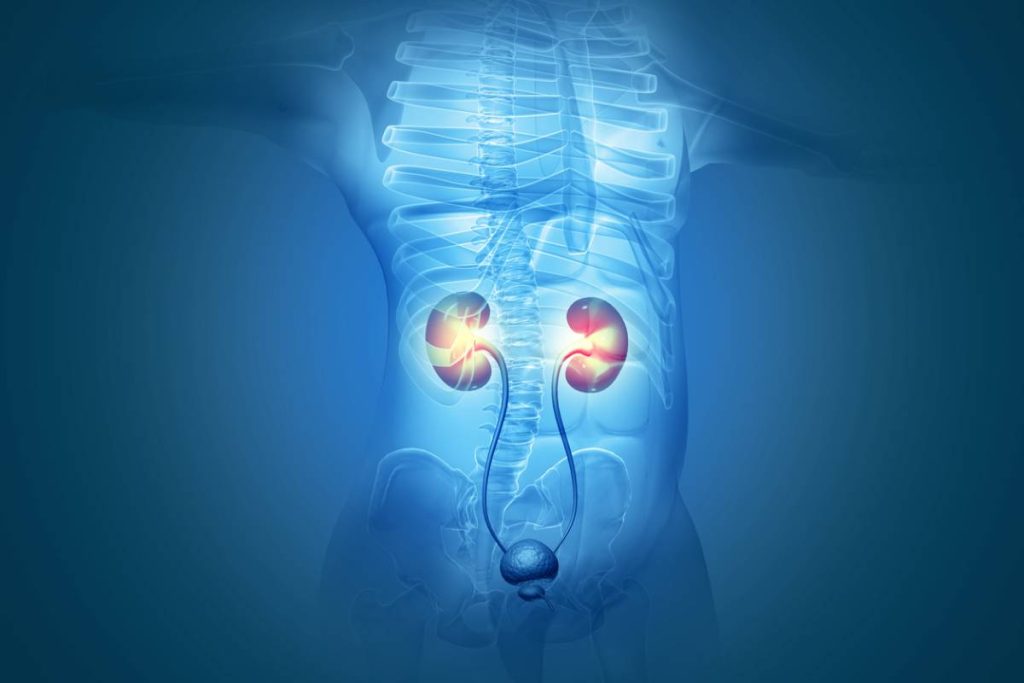
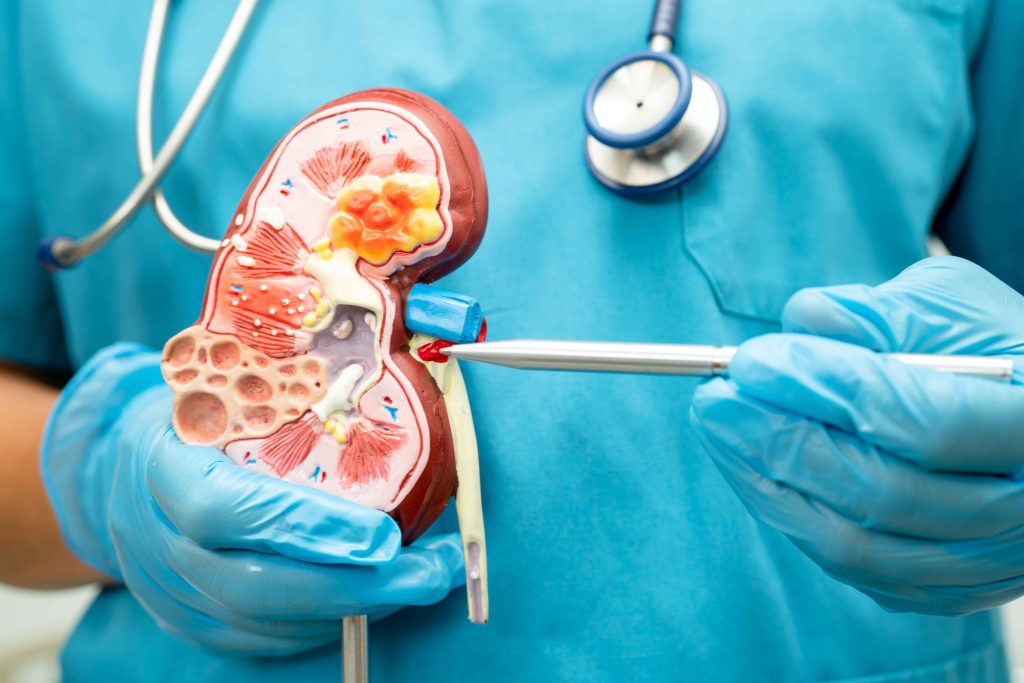
Nephrology and Pregnancy: Key Facts to Know
Many women learn about kidney health for the first time during pregnancy when routine tests reveal numbers or terms they have never heard before, raising questions about what these findings mean and how nephrology becomes part of prenatal care. Some describe this moment as both surprising and slightly unsettling because pregnancy already brings enough changes…
Read more